
Financial services organizations like banks, insurance, and investment banking are actualizing the best security solutions as they become more reliant on technology than ever.
Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley, BNP Paribas, JP Morgan, and others are enlisting cybersecurity talents swiftly. JP Morgan has an USD 11.5 billion technology budget of which spending on regulatory issues is growing more. Likewise, Citigroup spends USD 8 billion a year on the technology of which spending on protection is more than running or growing the firm.
Cybercrime, an offshoot of online dealings has compelled the financial sectors to prioritize cybersecurity. The concerns about cybercrime (29 percent) have leaped to fourth place from eighth in 2018, as per the bank’s Financial Institutional Survey. Given the gravity of the profession, the cybersecurity doyens are paid upwards of USD 0.3 to 0.6 million.
Let’s see why investment banks are becoming the targets for cyberattacks.
Investment banking is a high-profile financial services industry prone to sophisticated attacks. Many attacks arise due to business negotiations on pending M&A transactions and hefty deals.
Physical theft, computer fraud, cyber-attack, attack on servers to obtain customer’s personally identifiable information (PII) are the threats that are more visible in this sector. Moreover, technology adoption has led to increased data volume and the proliferation of endpoints. As a result, mobile devices, tablets, and other techno gadgets are spied for data held by the top management people.
Poor intelligence, management, and non-preparation for the prevailing attack ecosystem are the finger pointers while moving ‘digital’ or ‘on to the cloud’.
Improving cybersecurity is the rule at the moment for bankers, investors, asset managers, and intermediaries. Let’s walk through the best practices that will enable investment banking firms to secure their operations.
People, process, and technology form the main pillars to ensure a highly trusted firm. Technology must get implemented in investment banking while knowing how to manage the people managing it.
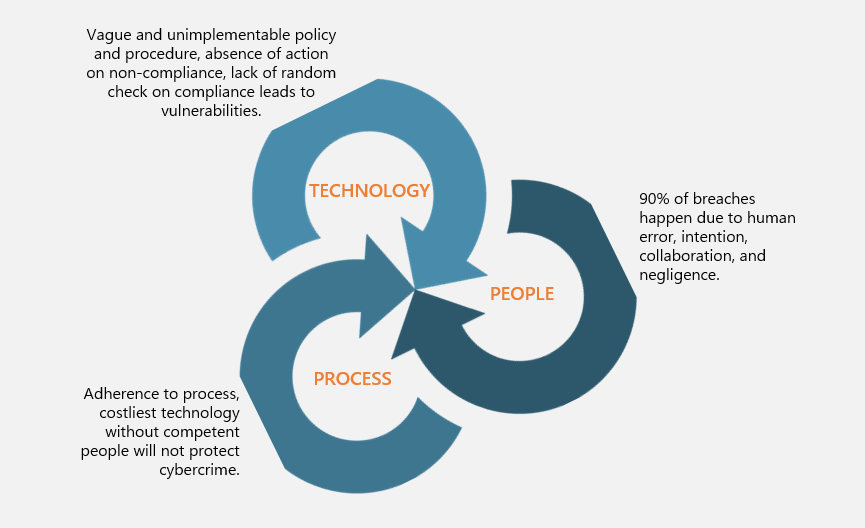
Here is the summary of best practices:
As far as human factors are concerned, security-sensitive investment banking firms must hold a security awareness program.
It is necessary to implement security practices based on awareness, alertness, accountability, belongings, and penalty for ignorance. Sadly, top-level executives share passwords with their assistants exposing the confidential data to unauthorized persons.
It is critical to train the employees at all levels on various policies, insider threats, and consequences.Regular awareness drive, administering separation of duties, monitoring of employee online activities, promoting good HR policies, and imposing a strong password must become the standard.
With ever-changing technology, security-related policies must get dynamic and enforceable as well. It must stress on core principles, actions, and guide decision-makers. The management must support security policies, include third-party service providers, employees, customers, and other related parties.
A few of the active measures to keep the ecosystem immune to attack are briefed here.
The investors search for organizations that have secure systems, generate profits, command a huge market share, valuation, and growth potential.
While Investment banking firms are transforming digitally, cybercriminals on the other side are exploiting vulnerabilities to access the system. To add to this, the prevailing COVID-19 crisis has hyped the situation bringing more concerns regarding security. The cost associated with these crimes can cripple the firm and lose clients’ interests.
It is pivotal to involve each of the employees in security practices and make them a strong link so that it gets harder to break the security chain. This calls for investment banking professionals with diverse skills like cybersecurity and other technical skills at a premium for investment banks.