
The merger of Vodafone India and Idea Cellular in 2018 symbolized a dramatic change in India's socio-telecom operation, which led to the formation of the country's biggest telecom company. Seeing the fierce competition and market disruption caused by Reliance Jio, both companies managed to benefit from this merger by joining resources to present a strengthened market front. The nature of the deal demonstrates the significance of M&A investment banking while also demonstrating how broad investment banking skills foster successful M&A in extremely competitive industries such as telecom.
The Vodafone India and Idea Cellular merger was influenced by numerous strategic business factors that impacted the structure of the telecom market in India. The two firms were already under a lot of pressure because of market competition, mainly due to the low prices offered by Reliance Jio. The pressure to compete within the market, which is slowly becoming more concentrated, was another reason for the merger.
Key strategic motivations included:
Investment banking skills were also important in assessing these synergies, managing the regulatory interface, and ensuring that the merger added value to the shareholders and kept the merged entity competitive.
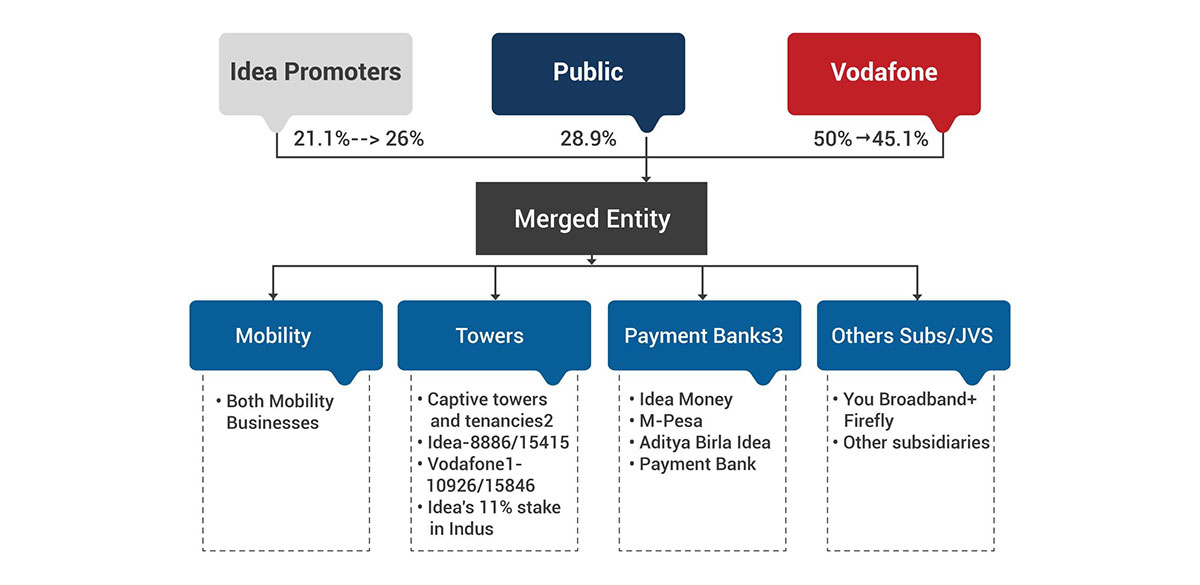
Vodafone India and Idea Cellular’s merger was one of the biggest mergers deals in the Indian telecom sector, paving the way for the largest telecom service provider in the country. The following is the timeline of this merger, and all these events were coordinated by M&A investment banking to enhance the whole process of the merger.
The two companies' management and the M&A investment banking teams had to work closely to ensure that this merger was carried out smoothly. This involved several processes, including regulatory approvals, due diligence, and valuation. It was a spectrum consolidation and financial restructuring deal that paved the way for emerging telecommunication giants in the market.
This merger profoundly affected the Indian telecom industry, turning the competitive landscape upside down and forming a stronger entity that challenges the market leader Reliance Jio. This consolidation led to several significant outcomes:
However, the post-merger landscape was not without challenges:
The Vodafone India – Idea Cellular merger was one of the most complex, high-profile deals in the Indian telecom sector, where M&A was instrumental throughout. Investment banks navigated the various challenges and intricacies of the deal, from initial negotiations to final approval.
Key areas where investment banking skills proved essential include:
In general, M&A education was critical in making the merger less complex and facilitating its successful completion.
Integration of Vodafone with Idea was a challenging task, both in terms of operations and finances. The merger of two large telecom operators with their own business model, culture, and technology required careful planning and smooth execution, for which M&A investment banks were often helpful.
Key challenges included:
The difficulties posed by the crisis were largely managed using the critical investment banking skills of restructuring the balance sheet, optimizing costs, and identifying synergy. Management's involvement ensured that the strategic goals were achieved in the merger and that risk was minimized in the post-merger integration phase.
The Vodafone India and Idea merger stands as a pivotal moment in India's telecom sector, creating the largest operator and reshaping the competitive landscape. With the deal, the M&A role is highlighted as a critical asset when dealing with highly complex transactions, including regulatory, financial, and strategic challenges. The merger illustrated how banks drive successful large-scale mergers by utilizing key investment banking skills like valuation, negotiation, and integration planning. Even as 5G comes into play, M&A will continue to play a big role in redefining the future of telecom across the world.