
Investment banks function under a clear division of work: the front, middle, and back offices. Each segment possesses a significant role geared towards achieving set goals regarding profitability, compliance, and efficiency in the company's operations. The front office is entirely responsible for revenue generation, the middle office deals with risk issues, and the back office efficiently processes various activities. It is crucial when aspiring to find out how to get into investment banking because it helps explain the level of employment and likely career opportunities within the banking industry.
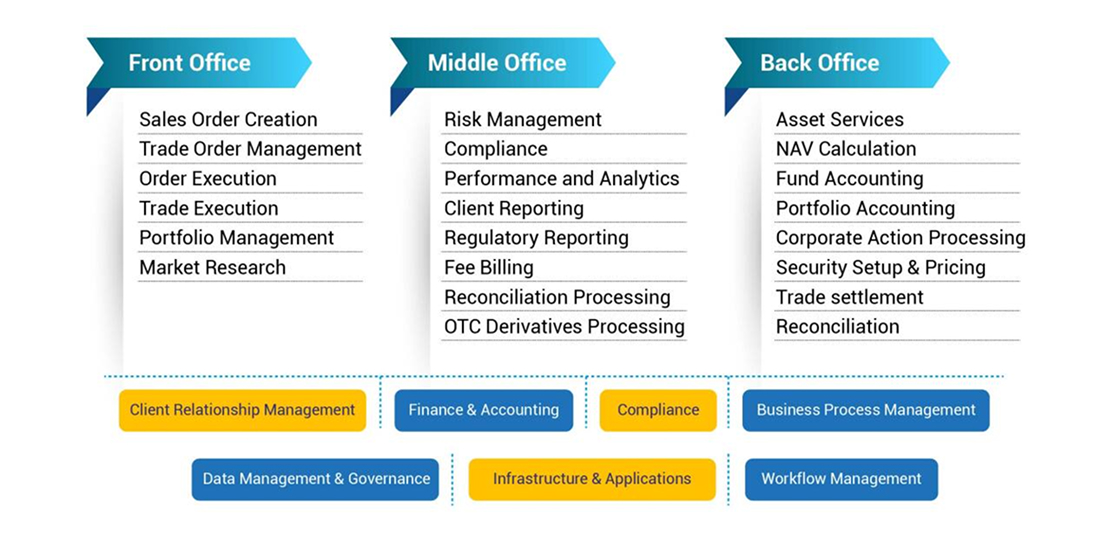
The front office is the nucleus of an investment bank's operations. It is most involved in direct client relations and managing crucial order delivery. Professionals in the front office are at the forefront of investment banking, making strategic decisions that shape the financial landscape.
Key Functions and Responsibilities of the front office are as follows:
Skills Required for a Front Office Role
Breaking Into the Front Office
The front office position requires a combination of expertise, networking, and adaptability. Candidates usually join an analyst or associate-level organization and use internships, university education, and networking to land jobs in this competitive field.
The middle office connects the front office to the back office and ensures that the complex and valuable transactions affected by the front office are done correctly and in compliance with the law. They are helpful in risk management, increasing compliance, and ensuring that all bank operations align with the firm's strategic objectives and minimize risks.
Some of the key responsibilities of the middle office are as follows:
Employees in the middle office should have adequate analytical abilities, proper problem-solving skills, and a keen understanding of financial laws and regulations and risk management standards. Such positions involve interaction with the front and back offices and mainly involve evaluating trends in economic data.
In an investment bank, the back office is sometimes referred to as the heart of the company. It provides essential operations and services to both the front and middle offices. The front office is mainly responsible for revenue generation and directly interacts with customers, while the middle office handles all risk and compliance issues.
The general responsibilities and activities of the back office are as follows:
Support positions are implied to be less high-profile than those in the offices, and they play a vital role in ensuring compliance with the necessary legal requirements and keeping operational costs down. Back-office employees provide crucial services for the bank’s operation, monitor its activity and compliance with legal acts, and ensure the operations' security. These functions are a starting point for the investment banking career, and those who perform well in these roles can transition to more direct-facing or officer-level jobs within the firm.
Its success depends mainly on the efficiency of the front, middle, and back-office departments. Different business departments must communicate effectively to meet clients’ needs, control risks, and avoid inconvenience factors in operations. Every office has a distinct feature as a business unit, but all function in relations where achievement depends on activity in the other.
The front office, middle office, and back-office structure is a convention that is central to investment banking and its daily functioning. These divisions assist the professionals in understanding their lifespan in the investment banking industry and advance strategically. While the front office generates profit, the middle office manages the risks, and the back office checks the solidity. Successful working and decision-making within an investment banking environment requires understanding the synergy between these functions to advance in a career.